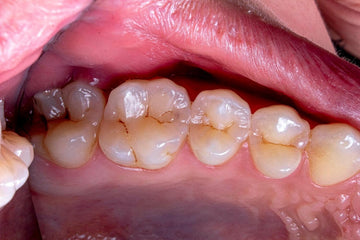
Bleeding gums: What causes it and treatment – All you need to know
Noticing a blood spot in the sink or your toothbrush can ring alarm bells. It’s important not to panic – bleeding gums are more common than you think.
Bleeding gums are often a sign that something isn’t quite right – it can be from simply not brushing your teeth enough to a more serious underlying condition.
In this article, Dr Sanjay Patel explores the possible causes of bleeding gums, when to be more concerned and the best ways to treat and prevent it from happening for a healthy smile.
What causes bleeding gums?
There are many reasons why gums may bleed – some are related to your hygiene, while others can be related to genetics, deficiencies or underlying conditions.
The main reasons are:
Poor oral hygiene
When you don’t brush your teeth enough – or with correct technique – plaque can begin to build around the gumline. This irritates the gums, causing inflammation and bleeding – you might notice this more when you’re brushing.
Gingivitis, Periodontitis and Trench mouth
When it comes to bleeding gums, it’s quite common that one of these conditions is the culprit.
· Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease. It’s characterised by swollen, tender gums that bleed easily.
· Periodontitis is a more advanced stage of gingivitis. When it’s advanced to this stage, the inner layer of the gum begins to pull away from the teeth. This opens up pockets that can bleed and become infected over time if not treated properly.
· Trench mouth is a severe, painful form of gum infection. It causes painful ulcers, bleeding, and bad breath and the root cause is often linked to poor oral hygiene or excessive stress.
You can read more information regarding these in our latest article “Gingivitis vs Periodontitis: Differences, Symptoms & Treatments”
Diabetes
One of the main symptoms of diabetes, other than trouble managing sugar levels, is a weakened immune system.
When the immune system isn’t functioning properly, the body has a reduced ability to fight off bacteria. This increases the likelihood of infection in the mouth and bleeding gums.
Vitamin K and C deficiencies
Vitamin deficiencies can cause gum bleeding in different ways.
Vitamin C is vital for your gum health and tissue repair. Lacking vitamin C means your body can’t repair damage in your mouth caused by trauma or plaque, resulting in bleeding.
Vitamin K is lesser known. However, your blood must help it clot when it needs to. A lack of vitamin K can cause thinning in the blood, which can exacerbate bleeding in your gumline.
Blood-thinning medications
If you’re on blood thinners, you might find that it becomes more noticeable if you already have bleeding gums.
Stress
Chronic stress weakens your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off gum infections. It may also lead to teeth grinding or clenching, which can further irritate the gums.
Trauma
Heavy impacts on the gums, like knocking them with a toothbrush, brushing too hard or aggressively or incorrect flossing, can all cause bleeding,
How bleeding gums are treated
If you already have bleeding gums – or they’re quite severe – you should consult your dentist or healthcare practitioner.
There are a variety of treatments available, and your dentist can help stop bleeding gums in their tracks.
Your dentist or healthcare practitioner will typically offer the following treatments to tackle bleeding gums:
Dental hygiene appointments
Depending on the severity of your bleeding gums, your dentist can help treat them with a professional cleaning. If you have severe bleeding gums, you may need a deep treatment that can involve procedures like root planing and tooth scaling.
The aim is to remove plaque and tartar buildup from below and around the gumline. Once this is gone, your gums can better heal without being irritated by plaque and debris, which reduces bleeding.
Antibiotics
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help treat an underlying infection that causes bleeding gums. Antibiotics help reduce the number of infection-causing bacteria in your mouth and gums, reduce inflammation and stop the bleeding.
Osseous surgery
Sometimes, gums are more prone to infection because the pockets around the tooth and gumline become stretched, opening the door to more infection-causing bacteria.
This procedure reshapes and cleans the bone around your teeth to reduce deepened gum pockets. This makes it easier to keep the area clean and naturally reduces the risk of infections and bleeding.
Laser periodontal surgery
If the condition causing bleeding gums has gone past the point of quick treatments, your dentist may recommend periodontal surgery.
This involves using precision lasers to target and remove diseased tissue and stimulate the healing process. Once healed, many people find their bleeding gum problems resolved.
How to stop bleeding gums at home
In the majority of cases, bleeding gums can be stopped at home by improving your oral care routine.
To stop or prevent bleeding gums at home, follow these crucial steps every time you brush.
· Brush your teeth a minimum of two times a day.
· Floss at least once a day at night time.
· Make sure you use fluoride toothpaste.
· Use an antibacterial or a gum-specific mouthwash while you experience bleeding gums to help fight plaque and freshen breath. It’s important to note that certain chlorhexidine mouthwashes can cause brown stains on teeth, so do not use them as a day-to-day mouthwash. Only as and when needed.
· Use an antibacterial mouthwash to help fight plaque and freshen breath.
· Steer clear of smoking to maintain a healthier mouth and brighter smile.
When should I be concerned about bleeding gums?
If you have bleeding gums, you should always consult your dentist as soon as possible – they can give you a thorough cleaning or give you the right hygiene advice to stop the problem at home.
However, you must seek treatment for these symptoms in particular, as the cause of your bleeding gums may stem from a more serious underlying condition that needs professional treatment.
Consult a specialist if you have:
· Bleeding happens regularly, even when you brush or floss gently and regularly to avoid bleeding.
· Your gums are red, swollen, or tender to the touch, as well as bleeding.
· You notice bad breath that won’t go away.
· You notice that your gums are lower than usual (receding gum line), or your teeth feel loose.
· You haven’t had a dental check-up in a while.
· You’re experiencing bleeding without brushing — while you’re eating, for example.
· You have other health conditions (like diabetes or are being treated with blood thinners).
FAQs
1. How long can I go with bleeding gums?
You shouldn’t wait long at all if your gums are bleeding. You should get it looked at as soon as possible.
It’s probably nothing serious, but bleeding gums are always the first sign of a lot of different conditions, as well as a lack of oral hygiene, so getting on top of it quickly can stop the problem from getting worse.
2. Are my bleeding gums caused by cancer?
Although bleeding gums are a symptom of some oral cancers, you shouldn’t panic straight away.
Your bleeding gums are much more likely to be caused by an easily treatable condition or a bad oral care routine than cancer.
3. What happens if you ignore bleeding gums?
If you ignore bleeding gums, you run the risk of them worsening and missing a treatable condition that could pose a serious problem in the future.
Bleeding gums are extremely common, but you shouldn’t ignore them because they can be caused by so many different things, some not serious, some life-threatening.